
The TÜV association presented a new cybersecurity study: 11 percent of German companies were affected by IT security incidents last year. The war in Ukraine and digital trends increase the risks. Phishing and ransomware were the most common attack vectors.
A good one in ten companies in Germany was affected by an IT security incident last year (11 percent). These are successful cyber attacks or other security-related incidents such as acts of sabotage or hardware theft. This was the result of a representative Ipsos survey commissioned by the TÜV association among 501 companies with 10 or more employees.
Cyber incidents: Around 50.000 incidents in Germany
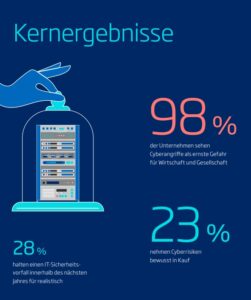
🔎 TÜV Association study: 23 percent of companies consciously accept cyber risks (Image: TÜV Association).
In absolute figures, this corresponds to around 50.000 incidents in this company size class. "Both the global political tensions and technological trends such as the spread of artificial intelligence pose a threat to the cyber security of companies in Germany," said Dr. Johannes Bussmann, President of the TÜV Association, at the presentation of the "TÜV Cybersecurity Study" in Berlin. "In addition to criminal hackers, state actors are stepping up their activities to obtain sensitive data, extort money or sabotage companies."
From the point of view of those surveyed, the greatest danger comes from organized cybercrime: 57 percent feel threatened by organized hacker gangs. 27 percent each see state-organized industrial espionage or politically motivated actors as a major threat. 22 percent fear so-called insiders who have internal knowledge of a company and can exploit it in an attack.
Majority expects more legal requirements
In view of the threat situation, a majority is in favor of additional legal requirements. 64 percent of respondents agree that every organization should be required to take appropriate cybersecurity measures. Bussmann: "Current legislative projects in the EU such as the Cyber Resilience Act in the area of product safety or the AI Act for artificial intelligence must now be passed quickly and applied quickly."
According to the survey results, the war in Ukraine has greatly increased the risk of cyber attacks in the German economy. 58 percent of companies in Germany share this view. And 16 percent have seen more cyber attacks or attempted attacks on their company since the outbreak of war. Large companies with 250 or more employees are hardest hit at 28 percent. Medium-sized companies follow with 20 percent (50-249 employees) and small ones with 11 percent (10-49 employees).
Phishing is the most common attack method
By far the most common attack method is phishing: e-mails with which passwords are tapped or malware is distributed. A phishing attack was successful in 62 percent of the companies affected. "Phishing takes on a new dimension with generative AI applications like ChatGPT," said Bussmann. "Soon there will be no more phishing emails that are easily recognizable due to errors or clumsy wording."
In second place are ransomware attacks, where IT systems are hacked, data is encrypted and companies are then blackmailed (29 percent). “Ransomware is a very successful method. Companies often pay to be able to work again quickly,” said Bussmann. Another popular scam is the manipulation of employees, the so-called social engineering (26 percent). A typical example is fake calls from IT support to obtain sensitive data. And 22 percent of the companies affected report a password attack in which access data was hacked.
Attacks: Serious consequences and financial damage
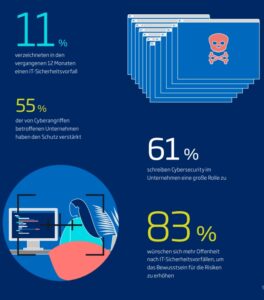
🔎 TÜV Association study: 11 percent of companies have experienced a cyber incident or hack in the last 12 months (Image: TÜV Association).
The consequences of the attacks are massive. 42 percent of the companies suffered financial losses, services for employees (38 percent) or customers (29 percent) could not be reached, production was down (13 percent) or sensitive data was stolen (13 percent). "Every year, cyber attacks in the German economy cause costs in the tens of billions," said Bussmann.
Companies counteract this with additional investments. Every second company has slightly or even significantly increased its spending on cybersecurity in the past two years (52 percent). Investments primarily go into modern hardware and software: 78 percent have decommissioned outdated devices, 71 percent have purchased secure hardware and 55 percent have introduced new cybersecurity software. 63 percent have improved the IT security of networked machines and systems. "There is still a lot of catching up to do here, because many machines and systems originally come from the analogue world," said Bussmann. "However, networking in the so-called Internet of Things has long been in full swing."
High investments in your own IT security know-how
In addition, the companies invest in their own know-how: 72 percent seek advice from external experts and 51 percent train their employees. "Practical exercises and certification are not yet widespread, but very effective," said Bussmann. Almost every third company uses so-called penetration tests, in which "good hackers" detect weaknesses in the IT systems (32 percent).
Do you have a moment?
Take a few minutes for our 2023 user survey and help make B2B-CYBER-SECURITY.de better!You only have to answer 10 questions and you have an immediate chance to win prizes from Kaspersky, ESET and Bitdefender.
Here you go directly to the survey
Almost a quarter carry out emergency drills to be better prepared for emergencies (24 percent). A quarter also introduced safety-related certifications (26 percent). They are based on norms and standards such as ISO 27001 or the IT basic protection of the BSI. "Norms and standards give companies orientation if they want to take a holistic approach and take their protection to a higher level," said Bussmann. “To the outside world, certification shows that a company or an individual product meets high IT security standards. This creates trust among business partners and consumers.” Almost every fourth company already fully complies with certain norms and standards (23 percent) and almost half are at least guided by them (46 percent).
80 percent: IT security is the basis for operations
Four out of five companies agree that IT security is the basis for smooth business operations (80 percent). 76 percent of those surveyed state that a high level of security is a competitive advantage for them and 69 percent that customers and partners demand a high level of cybersecurity. "The study shows that most companies have recognized the importance of IT security," said Bussmann. "Cybersecurity is relevant to business today." Smaller companies have some catching up to do. In companies with 10 to 49 employees, cybersecurity only plays a major role in half. And a good quarter of the little ones don't have the topic on their radar at all or don't think it's relevant (28 percent). In contrast, cybersecurity plays an important role for 80 percent of large and 76 percent of medium-sized companies.
Directly to the PDF study at TUEV-Verband.de
About TÜV association
The TÜV Association e. V. represents the political interests of the TÜV testing organizations and promotes the professional exchange of its members. He is committed to technical and digital security as well as the sustainability of vehicles, products, systems and services.
