Ransomware is a chronic threat. But their appearance is constantly changing. On the one hand, behind the permanent change there is a scene that is becoming more and more professional, thinks more economically or even politicizes itself in the current crisis. On the other hand, there are new technologies. Here Bitdefender shows four pillars for defending against extortion attacks.
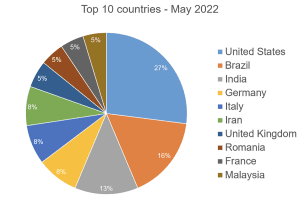
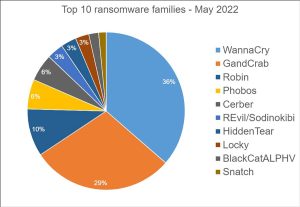
An effective defense must set up itself accordingly in depth and ward off the extortionate attacks in the various phases. The current Bitdefender Threat Report, which includes telemetry data from the previous month, shows for the month of May 2022 how active and diverse the ransomware scene is globally in 151 countries for which data is available. Unfortunately, Germany is among the leading countries in fourth place in the negative statistics: Eight percent of the detected ransomware attacks – not: infections – took place in this country.
Sophisticated Hacks
Attacks are becoming increasingly complex, targeted and long-term. There are also opportunistic mass attacks. After an automated scan of the target networks, they aim for quick success with a simple, immediate-acting ransomware.
However, ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) is predominant and a lot more dangerous. Cyber criminals use complex tools in a short-term business model. The actors in this RaaS ecosystem then split the ransom due. The ransomware operators who develop the malware and maintain the necessary infrastructure no longer have the highest share. The so-called "affiliates" are becoming more important: As independent contractors, they are the experts for compromising an IT network. They currently collect around 70 to 85% – or even more – of the ransoms paid. They hold the power in the ransomware economy, while the malware code becomes the raw material.
intrusion into the corporate network
The money ends up where the innovations take place – with the affiliates. These specialists use different technologies to compromise networks and find the data that victims are most likely to pay ransoms for.
They take their time maximizing damage. The first intrusion into the Internet via a phishing email may only be a matter of minutes. Hours or weeks then pass in order to prepare for the attack. The exfiltration, the encryption of the data and the extortion of the victims may not take place until months later.
Four pillars of ransomware defense
Depending on the phase, the attacks bypass different defense mechanisms. A well-positioned IT defense therefore fights ransomware in the various phases of the attack:
1. Prevention through a minimized attack surface
If you want to fend off ransomware attacks in advance, you have to do your homework. The management of IT security is part of the specification in order to reduce the IT attack surface. An IT administrator who continuously and conscientiously updates their network security and assets and checks configurations closes many loopholes for the blackmailers from the outset. Automated patching avoids the opening of security gaps. Zero-trust architectures ensure access control in advance.
2. Protection against infection on several levels
More complex Advanced Persistent Threats (APT) most likely cannot be stopped with conscientious IT administration alone. Attackers who are constantly looking for opportunities in a targeted manner use far-reaching technologies or take the detour via the software supply chain.
A defense in depth uses different IT security mechanisms to ward off an attack, for example via an e-mail infected with malware code, in the various attack phases (Figures 4 and 5):
- When receiving email: Email security relies on malware scanning, threat intelligence, and AI and machine learning to detect new attacks.
- After opening a document: Before running malicious macros, a security analysis in the isolated sandbox detonates the document and examines, for example, the effects of Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) code.
- When executing the VBA code: Numerous defense mechanisms protect the runtime environment, scan the working memory after unpacking and look for a code injection. They monitor an endpoint's processes in real time so that code activities do not go undetected.
- After nesting in the network: Network security recognizes patterns in data traffic when an endpoint with implemented malware contacts the command and control server in order to reload malicious code. The construction of a reverse shell by hackers is revealed by traffic patterns.
3. Reduction of the dwell time of the attackers
In an emergency, it is then important to quickly remove the hackers from the network. The longer attackers stay in the network, the more time they have for active reconnaissance. Businesses of all sizes need threat detection and response capabilities. In the case of advanced persistent threats, this is often difficult to achieve without managed detection and response (MDR) and without the help of external security experts. Threat hunting using a managed detection and response service also opens up the resources required for small and medium-sized companies that lack the skills, time and staff to set up an operationally efficient defense. With the help of experts, it will be possible to reduce the attackers' dwell time, thereby minimizing the damage they inflict.
But modern Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) or Extended Detection and Response (XDR) can also help by detecting malware on systems in the shortest possible time: To do this, it observes the behavior of the endpoints and reports a danger as soon as there is a likelihood of an attack. The cross-endpoint correlation of information helps to discover security-related incidents even faster.
4. Limit damage through automated backups
In a successful attack, reducing damage through emergency backups is key. Automated tools recognize an encrypted file by its entropy value. The higher, the greater the probability of encryption. Should an attack increase entropy, a ransomware protection tool automatically creates a temporary backup of the unencrypted file and restores it later. With this backup, however, neither shadow copies (volume shadow copies) nor other static backup solutions are the aim of the backup. Because the attackers have these places in the IT in their sights and usually encrypt them at the same time. Such automated backups protect the data against unknown attacks because the increase in entropy alone triggers the data to be backed up.
Many keys to security
Complex ransomware attacks cannot be defended against with a single defense mechanism. If you only rely on endpoint protection, you have a bad hand in the worst case. Protection against extortion attacks requires a multi-layered defense that includes the means of detection as well as recovery.
More at Bitdefender.com
About Bitdefender Bitdefender is a leading global provider of cybersecurity solutions and antivirus software, protecting over 500 million systems in more than 150 countries. Since it was founded in 2001, the company's innovations have consistently ensured excellent security products and intelligent protection for devices, networks and cloud services for private customers and companies. As the supplier of choice, Bitdefender technology is found in 38 percent of security solutions deployed around the world and is trusted and recognized by industry experts, manufacturers and customers alike. www.bitdefender.de