Jamf's new 2021 Security Report has some insights: Compromised mobile devices are accessing critical applications, smishing and Mac malware are on the rise, the human factor remains a major threat to IT security.
Jamf today announces its annual security report. It makes it clear that companies are confronted with increasing challenges in IT security: These include an increasingly mobile workforce, new strategies and goals of hackers and the persistent "human" vulnerability. Among other things, Jamf found that six percent of companies recorded a malware installation on a mobile device in 2021. One in four of these compromised devices continued to have access to email services. For the report in the last quarter of 2021, security researchers at Jamf Threat Labs examined more than 500.000 devices worldwide, including devices from Germany, Austria and Switzerland, that are managed and protected with Jamf.
Mobile workforce requires new security strategy
Mobile working continued to gain ground last year. The dangers for the IT infrastructure of companies also increased accordingly: Six percent of companies recorded a malware installation on a mobile device last year - twice as many as in the previous year 2020 (three percent). Significantly more devices were not compromised but at risk: 39 percent of companies regularly used an operating system with a known vulnerability, an increase of 2020 percentage points compared to XNUMX. Around one in ten companies (XNUMX percent) had a potentially unwanted application in them installed in the device fleet, more than twice as many as in the previous year (five percent).
39 percent use an operating system with a security vulnerability
While the percentage of compromised or compromised devices seems small, it's alarming how many of those devices are accessing sensitive data. Seven percent of the compromised devices continued to access cloud storage services such as OneDrive, GoogleDrive or Dropbox. Nine percent used a CRM such as Salesforce or Microsoft Dynamics. 25 percent used email services. Around a third (34 percent) accessed conferencing solutions such as Zoom or Microsoft Teams. The numbers increase significantly when not only compromised but also vulnerable devices are included in the analysis:
- Access to cloud storage services – 9 percent
- Access to CRM solutions – 15 percent
- Use of email services – 48 percent
- Use of conferencing services – 64 percent
The results underscore the need to adapt security strategy to an increasingly mobile workforce. Instead of traditional solutions that focus on protecting the systems within the office and the company network, decentralized security concepts are used that can check access authorizations in real time, such as Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA).
Hackers adapt their strategies: different tools, different goals
While companies adapt their IT security to the new circumstances, hackers have also developed new strategies. They no longer rely solely on malware, but access data elsewhere. This explains why the number of confirmed malware infections is low, but malicious network traffic is observed far more frequently: 36 percent of companies encountered indicators of malicious network traffic on a mobile device in 2021. These indicators include things like data exfiltration or connections to command-and-control servers or websites known to harbor malware.
At the same time, phishing attacks are increasing. They are often designed to spy on login credentials for cloud services. With relatively little effort, hackers gain access to important and sensitive data. They use well-known brands: 43 percent of the campaigns used Apple, 27 percent Paypal and nine percent Amazon to trick their victims into trusting them. Smishing, i.e. SMS-based phishing, is also in vogue. According to data from Jamf Threat Labs, one in ten users is a victim of such attacks.
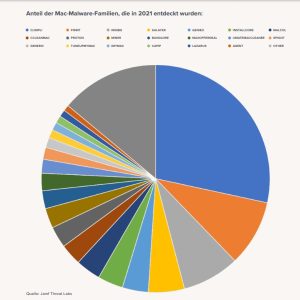
Not only are hackers using new tools, they are also looking for new targets: the analysis revealed the increasing spread of Mac malware. Mac malware families Cimpli, Pirrit, Imobie, Shlayer, and Genieo are among the top 5 that attempted to compromise Jamf-protected devices in 2021.
End users remain the greatest threat to data security
The IT security of an organization is still largely dependent on the end device users. This is not only shown by the success of phishing campaigns: in every third company (29 percent) at least one user fell for a phishing attack in the past year. The analysis also revealed that two percent of devices used for work had the screen lock disabled – a mistake that can have serious consequences if the device is lost or stolen. The number of devices connecting to risky hotspots, such as at the airport or in a coffee shop, also increased. One percent of the devices made such a connection every week, twice as many as in the previous year.
About the report
Jamf's 2021 Security Report summarizes the results of an analysis of 500.000 devices protected by Jamf. It is a sample from 90 different countries and from different operating systems (iOS, macOS, Android and Windows). The results refer to a period of 12 months, the analysis itself was carried out in the fourth quarter of 2021. The metadata analyzed in this research comes from aggregated logs that do not contain any personal or organization-identifying information.
More at Jamf.com
About Jamf
Jamf, the standard in Apple enterprise management, extends the Apple Experience that consumers love to businesses, schools, and government organizations. Around 100.000 IT experts exchange ideas and best practices in the world's largest Apple community forum, Jamf Nation. Currently, more than 60.000 companies from over 100 countries rely on Jamf to successfully manage their Apple devices.