On May 1, 2023, the amendment to the IT Security Act 2.0 will come into force. When the transition period expires, the BSI is demanding new requirements from operators of critical infrastructure. What that will be in detail, who will be affected and what measures must be taken by then. A comment from Radar Cyber Security.
Cyber criminals are increasingly targeting operators of critical infrastructures and companies with particular economic importance. This can not only lead to production losses worth millions and supply bottlenecks, but in the worst case it can endanger public safety. In addition, KRITIS operators not only have to protect themselves against monetarily motivated blackmail attempts. Politically motivated attacks as part of hybrid warfare have also become a real threat.
ITSig 2.0 – IT Security Act 2.0 from May 2023
The German legislator reacted to these dangers as early as 2021 with the Second Act to Increase the Security of Information Technology Systems - in short: IT Security Act 2.0. With this, the existing BSI law was supplemented by further points. A second Network and Information Security Directive (NIS 2) will also follow suit at EU level.
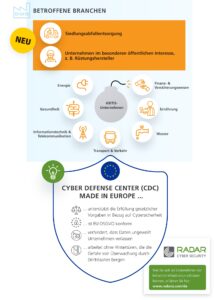
In addition to the traditional KRITIS operators, companies in the so-called "special public interest", such as armaments manufacturers or companies with particularly great economic importance, must now also implement certain IT security measures. As a result, the circle of critical infrastructures was expanded to include sectors such as waste disposal and armaments production.
IT Security Act 2.0: New requirements at a glance
- Critical infrastructure operators must implement attack detection systems by May 1, 2023 at the latest.
- KRITIS operators must notify the Federal Ministry of the Interior of the planned initial use of critical components, for example if the manufacturer is controlled by a third country or contradicts security policy goals of the German Federal Government, the EU or NATO.
- Companies in the special public interest are obliged to regularly submit a self-declaration. They have to explain which certifications in the field of IT security have been carried out in the last two years and how their IT systems have been secured.
Measures to protect critical infrastructure
KRITIS operators and companies that need to protect their IT and control technology from cyber attacks need integrated solutions that are in line with the IT Security Act 2.0, the BSI Act and the ISO standard 27001 on information security. The following detection modules should therefore be used on the technology side:
- Log data analysis (LDA) / security information and event management (SIEM): This means the collection, analysis and correlation of logs from a wide variety of sources. This results in alerts for security problems or potential risks.
- Vulnerability Management & Compliance (VMC): Vulnerability management enables continuous, internal and external vulnerability scanning with comprehensive detection, compliance checks and tests for complete coverage. As part of software compliance, the authorized use of software for each server or server group is determined using a set of rules and continuous analysis. Manipulated software can be recognized quickly.
- Network Condition Monitoring (OT module): This reports real-time communications that indicate a disruption to error-free operation. Technical overload conditions, physical damage, misconfigurations and deterioration in network performance are thus recognized immediately and the sources of error are identified directly.
- Network Behavior Analytics (NBA): With network behavior analysis, the detection of dangerous malware, anomalies and other risks in network traffic is possible based on signature and behavior-based detection engines.
- Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR): Endpoint Detection and Response stands for the analysis, monitoring and detection of anomalies on computer computers (hosts). With EDR, active protection actions and instant alerting are provided.
Due to the complexity, the further processing of the security-relevant information from these modules is carried out by security specialists. You evaluate and prioritize the automatically gained insights from a huge data collection. The results of this analysis are the basis for initiating the right countermeasures by in-house specialists.
In order to ensure the best possible data security, it is also recommended to set up on-premise solutions as the most secure form of deployment. Even if the trend is increasingly towards the cloud, this is problematic in terms of the high level of data sensitivity in the area of KRITIS.
Cyber Defense Centers (CDC) to protect critical infrastructure
With a Cyber Defense Center (CDC) - also known as a Security Operations Center (SOC) - KRITIS operators and companies can effectively implement all of the above points in order to implement a consistent, integrated security concept for their IT and OT infrastructure. A CDC encompasses technologies, processes, and experts responsible for monitoring, analyzing, and maintaining an organization's information security. The CDC collects real-time data from the organization's networks, servers, endpoints, and other digital assets and uses intelligent automation to detect, prioritize, and respond to potential cybersecurity threats - XNUMX/XNUMX. This allows threats to be contained and neutralized quickly.
In addition, the use of European security technologies for KRITIS operators and companies in the particular public interest is recommended. In this way, legal data protection requirements can be easily met. These include, for example, the requirements of the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the requirement of the BSI law for suitable proof of your precautions to avoid disruptions to the availability, integrity, authenticity and confidentiality of your information technology systems, components or processes that are necessary for the functionality of the critical infrastructures operated by them are relevant.
Attacks on Europe's KRITIS will increase
The use of European security technology also makes it easier for the BSI to check critical components to ensure that third-country actors cannot access sensitive information in violation of EU data protection at any time. This is all the more important in times when the Privacy Act between the USA and Europe is inactive.
It is to be expected that attacks on Europe's critical infrastructure will continue to increase in the future and this is particularly evident on the geopolitical stage with the Ukraine war. With a holistic Cyber Defense Center solution, German KRITIS operators can significantly increase their cyber resilience in order to defend themselves against attacks.
More at RadarCS.com
About Radar Cyber Security Radar Cyber Security operates one of the largest cyber defense centers in Europe in the heart of Vienna based on the proprietary Cyber Detection Platform technology. Driven by the strong combination of human expertise and experience, paired with the latest technological developments from ten years of research and development work, the company combines comprehensive solutions for the challenges related to IT and OT security in its products RADAR Services and RADAR Solutions .