
After the large waves of ransomware and the far-reaching changes in IT landscapes caused by the COVID pandemic, the geopolitical consequences of the Ukraine war are now also causing many organizations to have to make further adjustments to their cyber defense systems. The new IDC study "Cybersecurity in Germany 2022" has revealed how organizations want to deal with the new framework conditions and what hurdles have to be overcome.
In September 2022, IDC surveyed security managers from 206 companies with more than 100 employees across all sectors in Germany in order to gain detailed insights into the challenges, procedures and plans for setting up and operating security landscapes in the context of current IT and business developments receive.
Ransomware: Majority is willing to pay the ransom
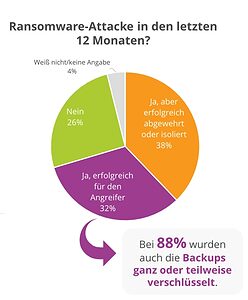
🔎 Out of 70 percent of the attacked companies, only a little more than half were able to fend off the attack (picture IDC).
Ransomware is still a major threat. 70 percent of the organizations surveyed were affected in the last 12 months. About 38 percent were able to fend off the attacks or isolate them in good time. 32 percent fell victim to a ransomware attack. But it gets even worse: for almost all victims, the backups were partially or even completely encrypted, thus preventing comprehensive recovery.
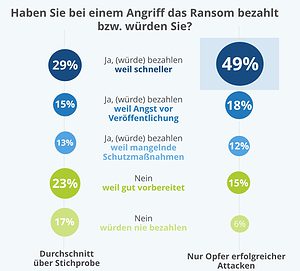
The survey shows that 49 percent of victims pay because "it's just faster". A further 18 percent fear that their data will be published. The bottom 12 percent are afraid to admit they used inferior protections. In Germany, therefore, the ransomware attackers do a good and quite secure business. Other countries are further along, such as the US, where paying ransomware ransoms is already banned, with only a few exceptions.
This is also fundamentally correct from a business continuity perspective, but here IDC believes that more effort and investment in your own permanent protection and backup measures would be more sensible and sustainable - especially since payment is no guarantee of successful decryption.
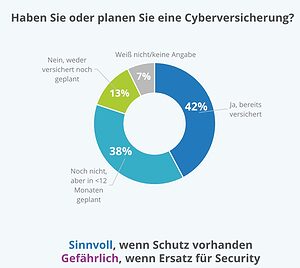
80 percent plan or use cyber insurance
Companies are already insured or plan to be within the next 12 months. Especially those without successful ransomware defenses often have or plan to have insurance. This suggests that many see cyber insurance as a substitute for security measures. However, IDC warns against thinking this way, because cyber insurance cannot prevent damage, only reduce or compensate for the economic losses. Insurance cannot replace lost trust and reputation.
Cloud security is a priority for every third company
Among the strategic security topics, cloud security stands out, which is by far the most common priority for companies at 36 percent. "The increasing use of the cloud for more and more critical processes and the resulting increase in dependency coupled with an increase in the level of threats makes extensive measures to protect them absolutely necessary," says Marco Becker, Consulting Manager at IDC and head of the study.
At 22 percent, endpoint security is the second most common top challenge. The increasing use of end devices for remote work and the strong decentralization of endpoints through the (industrial) Internet of Things and Edge Computing increase the risk potential. Secure backups and disaster recovery are in third place with 19 percent.
This priority is mainly due to the great success of ransomware and, according to IDC, is justified because in 88 percent of successful ransomware attacks on study participants, the backups were also fully or partially encrypted. At nine percent, security automation and orchestration gets a little too little attention. "Measured against the complexity of security and the shortage of skilled workers, this topic should be given much more attention," advises Becker.
Conclusion: Without action, defeat is imminent
In the opinion of IDC, even after analyzing this year's study results, there is still a lot of potential for improvement when it comes to improving cyber security. Standard solutions and a fundamentally good understanding of the problems and security challenges are available in most companies, but now it is important to use existing security solutions effectively.
From IDC's point of view, the reduction of security complexity is one of the most important adjustment screws. A second problem area is the increasing shortage of personnel and specialists for security. IDC does not assume that this will improve in the short term but will continue to worsen. Above all, the interaction of complexity and the shortage of skilled workers is highly dangerous: Both catalyze each other, because the greater the complexity, the more staff is needed to master it, and the greater the shortage of skilled workers, the less can be done to counteract the complexity.
Without a smart mix of intensive education and training for security personnel, increased investments in security automation, orchestration and intelligence and supplementing their own security skills with external security infrastructures and services, IDC believes that many organizations run the risk of losing control in the race against cybercriminals.
Management must take on more responsibility
For this it is essential that the management and board of directors finally take on clear responsibility for security and promote a holistic cybersecurity culture and the integration of business and cybersecurity. The increasing dependency on IT when designing the customer experience, the geopolitical consequences of the Ukraine war and the sharp increase in commercial cybercrime make maintaining the increasingly important digital trust of customers and partners essential for business. While some IT measures are being postponed for the time being in the shadow of the crises, cyber security is more important and urgent than ever as a guarantor for one's own security and for securing one's existence.
More at IDC.com
About IDC Central Europe
IDC is the world's leading provider of information technology and telecommunications market intelligence, consulting services and events. IDC analyzes and forecasts technological and industry-related trends and potentials, enabling its customers to plan their business strategies and IT purchasing in a well-founded manner. Through the network of more than 1100 analysts in over 110 countries with global, regional and local expertise, IDC can provide its customers with comprehensive research on the most diverse segments of the IT, telecommunications and consumer market. For more than 50 years, business leaders and IT leaders have trusted IDC to make decisions.

2 thoughts on "Cybersecurity 2022: almost 80 percent of ransomware victims pay"
Comments closed