
Although thousands of vulnerabilities caused by CVEs are known, these have been found 2,3 billion times as vulnerabilities in companies and authorities worldwide. The 2023 TruRisk Research Report focuses on the 163 most critical or highly dangerous vulnerabilities and evaluates them.
In its 2023 TruRisk Research Report, Qualys publishes interesting evaluations. The research report provides an overview of known security vulnerabilities found by Qualys in 2022 at companies and governments worldwide - more than 2,3 billion. The results of the study underline the image of opportunistic attackers who are constantly changing their techniques in an agile manner in order to successfully exploit security gaps.
Security gaps as a gateway
Businesses and governments are increasingly driving digital transformation to increase productivity, and new software tools to support these initiatives and programs are being developed at a faster pace than ever before. With rapid technological progress, however, the number of software vulnerabilities is also increasing, which pose a significant risk to IT environments.
Qualys is committed to helping organizations reduce their cyber risks. In line with this, the Qualys Threat Research Unit (TRU) has conducted in-depth investigations into the more than 13 trillion events tracked by the Qualys cloud platform. The evaluation of the anonymized detection data provides insight into the security gaps found on the devices, the security of web applications, configuration errors in locally installed devices and the state of cloud security. Analysis of this vast knowledge base, coupled with TRU's unique view of threat actor activities before and after exploitation, resulted in five "Risk Facts".
Risk Fact #1
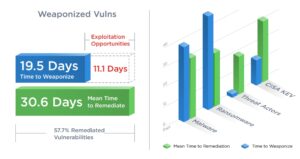
🔎 In just 19,5 days, attackers finished an exploit. Companies need 30,6 days to patch, but only 57,7 percent actually do this (Image: Qualys).
Speed is key to outmaneuvering opponents
Vulnerabilities for which an attack vector has been developed are patched within 30,6 days on average, with only 57,7% of vulnerabilities closed in real terms during this time. In contrast, the attackers only need an average of 19,5 days to develop a way of attacking these vulnerabilities. According to this, the attackers have 11,1 days to exploit the vulnerabilities before the companies close them.
Risk Fact #2
Automation makes the difference between success and failure
The research found that patches that could be installed automatically were deployed 45% more often and 36% faster than manually installed patches. Vulnerabilities that could be patched automatically were remediated in an average of 25,5 days, while manually patched vulnerabilities took 39,8 days to remediate. The patch rate for automated patches was 72,5% versus 49,8% for manual patches.
Risk Fact #3
Initial Access Brokers (IAB) attack what the companies ignore
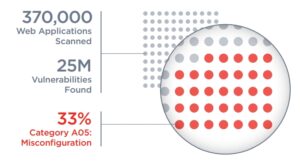
🔎 33 percent of the vulnerabilities found in web applications are due to misconfigurations (Image: Qualys).
A growing trend in the threat landscape are so-called initial access brokers (IABs), sometimes referred to as "affiliates". As the report shows, companies are now patching Windows and Chrome faster, forcing attackers - and the IAB in particular - to exploit vulnerabilities beyond the "Big Two". The average time to remediate IAB vulnerabilities is 45,5 days compared to 17,4 days for Windows and Chrome. Patch rates are also lower for IAB gaps: 68,3% of them are patched; for Windows and Chrome it is 82,9%.
Risk Fact #4
Misconfigurations in web applications are still commonplace
The investigation also included anonymized detections by the Qualys Web Application Scanner, which scanned 2022 web applications worldwide in 370.000 and correlated the data with the OWASP Top 10. The scans uncovered more than 25 million vulnerabilities, 33% of which fell into the OWASP Category A05: Misconfiguration. These misconfigurations offered attackers a gateway to inject malware into around 24.000 web applications.
Risk Fact #5
Misconfigurations in infrastructure open the door to ransomware
The TRU evaluated all controls that failed more than 50% of the scans and the MITER ATT&CK techniques associated with each of those specific controls. In terms of cloud misconfigurations, the controls that failed were most commonly associated with the following three MTRE ATT&CK techniques: T1210: Exploitation of Remote Services, 1485: Data Destruction, and 1530: Data from Cloud Storage Object.
This shows that cloud misconfigurations put organizations at risk of service exploitation and data being encrypted and leaked. The three techniques are exactly how ransomware works today. Scans for these configuration errors only had a 49,4% success rate; more than half were therefore failed. Attackers can exploit these misconfigurations to move sideways through an environment.
More at Qualys.com
About Qualys
Qualys is a pioneer and leading provider of disruptive, cloud-based IT, security and compliance solutions. The company has more than 10.000 active clients worldwide, including the majority of the Forbes Global 100 and Fortune 100 companies. Qualys helps organizations streamline and consolidate their security and compliance solutions into a single platform, enabling greater agility, better business outcomes and significant cost reductions.
