
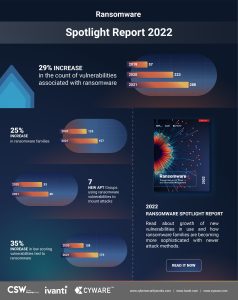
Hackers are increasingly targeting zero-day vulnerabilities and the supply chain. 29% more ransomware associated CVEs and 26% more ransomware families compared to last year. These are just some findings of Ivanti Ransomware Report 2022.
Security vendor Ivanti has released the results of the Ransomware Spotlight Year End Report, conducted jointly with Cyber Security Works, a CNA (Certify Numbering Authority) and Cyware. The report identifies 32 new ransomware families in 2021, bringing the total to 157, an overall 26% increase year-on-year. The report shows that these ransomware groups are increasingly targeting unpatched vulnerabilities. They are also extremely quick to weaponize zero-day vulnerabilities to launch serious attacks. At the same time, they are expanding their attack vectors and finding new ways to compromise corporate networks and trigger attacks with far-reaching consequences.
The most important findings and trends of the report
Unpatched vulnerabilities remain the top attack vectors used by ransomware groups.
The analysis uncovered 65 new vulnerabilities associated with ransomware last year. This corresponds to an increase of 29% compared to the previous year. This brings the total number of ransomware-related vulnerabilities to 288. Alarmingly, over a third (37%) of these newly added vulnerabilities were trending topics on the dark web and were repeatedly exploited. In parallel, 56% of the 223 legacy vulnerabilities identified prior to 2021 were still actively exploited. This shows that organizations need to prioritize and patch the vulnerabilities targeted by ransomware groups, whether they are newly identified or legacy vulnerabilities.
Ransomware groups are already finding and exploiting vulnerabilities
And that's before those CVEs are added to the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) and patches are available. QNAP (CVE-2021-28799), Sonic Wall (CVE-2021-20016), Kaseya (CVE-2021-30116) and most recently Apache Log4j (CVE-2021-44228) vulnerabilities were used for attacks even before they were published in included in the National Vulnerability Database (NVD). This dangerous trend underscores the need for vendors to react quickly when vulnerabilities are disclosed and patches released. It also shows that companies cannot rely on NVD alone. Therefore, when prioritizing which vulnerabilities to patch, they should also keep an eye on vulnerability trends, examples of vulnerabilities exploited, vendor notices, and security agency alerts.
Ransomware groups are increasingly targeting supply chains
A single breach within a supply chain can open up multiple avenues for threat actors to hijack the entire system distribution across hundreds of victim networks. Over the past year, threat actors have successfully demonstrated this via vulnerabilities in third-party applications, proprietary products, and open-source libraries. For example, the REvil group targeted the CVE-2021-30116 vulnerability in the Kaseya VSA remote management service. To do this, it used a malicious update package that compromised all companies using on-premise and cloud versions of the VSA platform.
Ransomware groups are increasingly making their attack vectors available as a service
Ransomware-as-a-Service is a business model where ransomware developers offer their services, variants, kits or code to other hackers in exchange for payment. Exploit-as-a-Service solutions allow threat actors to rent zero-day exploits from developers. In addition, droppers-as-a-service allow novices to spread malware via programs. And Trojans-as-a-Service, also known as Malware-as-a-Service, allows anyone with an internet connection to source custom malware and distribute it in the cloud with no installation required.
With 157 ransomware families exploiting 288 vulnerabilities
Along with Ivanti, Cyware, provider of Cyber Fusion, next-generation SOAR, and threat intelligence solutions, and Cyber Security Works helped create it. As a certificate authority, the company is responsible for regularly assigning CVE IDs to vulnerabilities.
Assessments and recommendations of the study authors
Srinivas Mukkamala, senior vice president of security products at Ivanti
“Ransomware groups are becoming more sophisticated and their attacks more powerful. These threat actors are increasingly turning to automation to exploit vulnerabilities and penetrate deep into compromised networks. They are expanding their targets and launching more attacks on critical infrastructure and supply chains. Remediating weaponized vulnerabilities without delay requires a combination of risk-based vulnerability prioritization and automatic patch intelligence. The goal must be to identify and prioritize vulnerabilities and accelerate resolution.”
Anuj Goel, CEO of Cyware
“The main shift we are seeing in the ransomware landscape is that attackers are trying to subvert processes like patch deployment. At the same time, they look for gaps in the protection measures to penetrate systems. The discovery of vulnerabilities must be responded to with an action that treats vulnerability data as information in order to make quick response decisions. As ransomware groups operationalize their tools, methods, and target lists, it is imperative for SecOps teams to automate processes for vulnerable assets and systems to heal themselves. The risk can only be reduced by operationalizing information in real time.”
Aaron Sandeen, CEO of Cyber Security Works
“Ransomware is devastating to customers and employees in every industry. In 2022, we will continue to see a proliferation of new vulnerabilities, exploit types, APT groups, ransomware families, and CWE categories. Likewise, old vulnerabilities remain the focus of criminals. Ultimately, leaders need innovative and proactive help to prioritize and eliminate ransomware threats.”
Background of the study
The Ransomware Index Spotlight Report is based on data from a variety of sources, including proprietary data from Ivanti and CSW, publicly available threat databases, and threat research and penetration testing teams. The entire report is also available for download.
More at Ivanti.com
About Ivanti The strength of unified IT. Ivanti connects IT with security operations in the company in order to better control and secure the digital workplace. We identify IT assets on PCs, mobile devices, virtualized infrastructures or in the data center - regardless of whether they are hidden on-premise or in the cloud. Ivanti improves the provision of IT services and reduces risks in the company on the basis of specialist knowledge and automated processes. By using modern technologies in the warehouse and across the entire supply chain, Ivanti helps companies improve their ability to deliver - without changing the backend systems.
